| Definition: | law giving the spectral concentration of radiance of a Planckian radiator as a function of wavelength and temperature(1)
X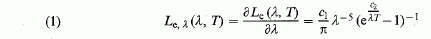
Le, radiance
λ, wavelength in vacuum
T, thermodynamic temperature
c1 = 2πhс2o
c2 =hсo/k
h, Planck's constant
co, velocity (speed) of light in vacuum
k, the Boltzmann constant
NOTE 1 – The formula is sometimes written with X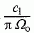 instead of X instead of X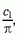 , where Ω0 is the solid angle of magnitude 1 steradian. , where Ω0 is the solid angle of magnitude 1 steradian.
NOTE 2 – For a detector in a medium of refractive index n, the measured radiance is :
n2 Le, λ(λ, T)
NOTE 3 – Planck's law can be also expressed to give the spectral concentration of radiant exitance Me, λ(λ, T); the first factor in the formula (1), is then c1 instead of c1/π.
NOTE 4 – Both quantities (radiance and exitance) apply to the unpolarized radiation as emitted.
|